Here is the center of mass of a semicircular and annular semicircular disc.
Center of Mass of Semicircular Disc
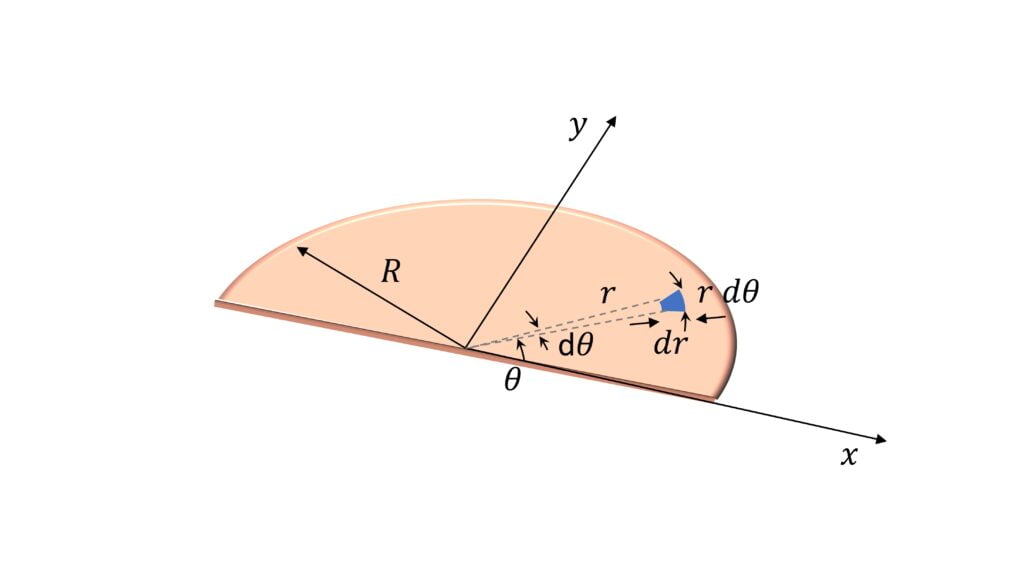
$x_{cm} = 0$
$y_{cm} = \cfrac{4R}{3 \pi}$
Center of Mass of Annular Semicircular Disc
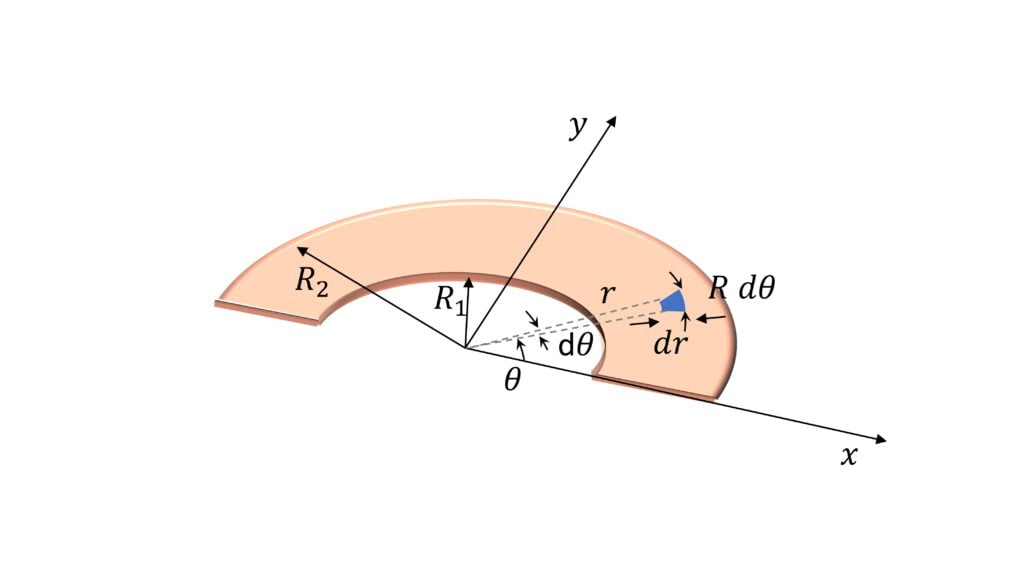
$x_{cm}=0$
$y_{cm} = \cfrac{4}{3 \pi} \cfrac{R_1^2 + R_1 R_2 + R_2^2}{R_1+R_2}$
To continue to explore center of mass of other commonly encountered shapes, click here…
- Two Particle System
- System of Three Particles
- A group of simple rigid bodies (for example a uniform $I$ shaped lamina
- Non uniform rod of length $L$
- Arc
- Uniform Circular arc
- Semicircular ring
- Semicircular disc
- Annular semicircular disc
- Triangle
- Solid hemisphere
- Hollow hemisphere
- Hollow cone
- Solid cone

